ADHD and medication in adult treatment
DESCRIPTION:
How do ADHD medications really work? Learn all about methylphenidate & co., motivation and sleep in ADHD. Find out about effects and side effects now!
ADHD and medication in the treatment of adults: How ADHD medication really works and what side effects occur
For a long time, there was a clear picture of how ADHD was treated: psychostimulants such as methylphenidate or lisdexamfetamine act directly on the attention centres in the brain; however, a recent large-scale study from 2025 revises this understanding. For adults with ADHD, this means an entirely new understanding of their medication.
How ADHD medication works: motivation instead of focus
Contrary to the old assumption, brain research shows that the medication does not primarily "repair" the attention circuits directly. Instead, the active ingredient influences systems for arousal (alertness) and reward.
Its effectiveness is based on inhibiting the reuptake of dopamine and noradrenaline in the synaptic cleft. This mix of neurotransmitters raises the brain's expectation of reward.
· The effect: a task feels less tedious. You are more likely to start and stick with it longer.
· The finding: drug therapy does not so much increase mental capacity as it does the willingness to expend energy.
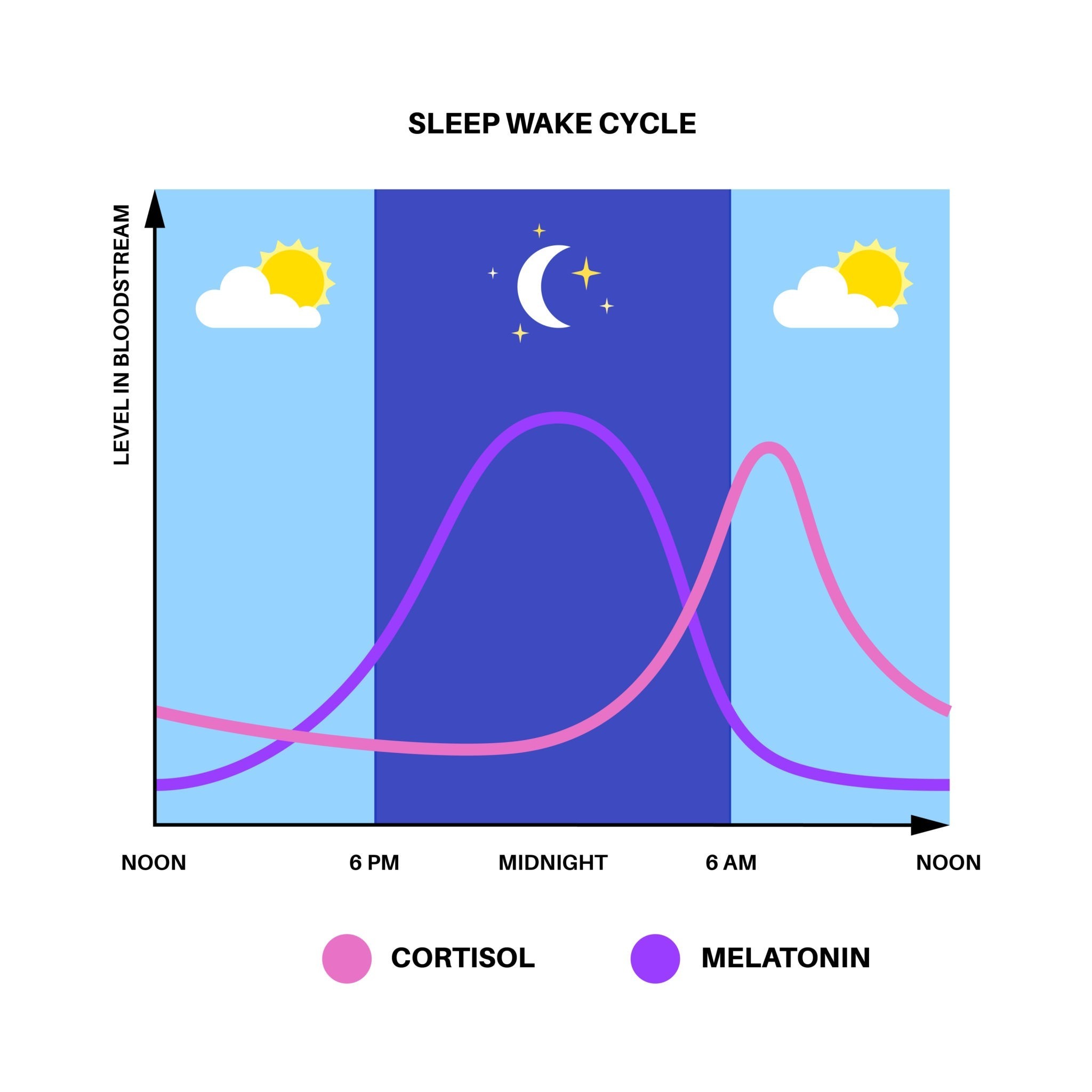
Treatment of ADHD in adults: medication and sleep
A key issue in adult ADHD is exhaustion. The study shows that ADHD medication works by masking sleep deprivation. When psychostimulants such as Ritalin or Medikinet Adult are taken, the typical brain patterns associated with fatigue disappear. This is a double-edged side effect: you feel capable of performing, even though your body needs to regenerate.
AuDHS: When ADHD is treated with medication
For people with AuDHS (autism & ADHD), taking medication is often more complex. When the chaos of ADHD is reduced by methylphenidate or another active ingredient, autistic traits usually become more pronounced. Sensory sensitivity may increase as the "distracting" filter of ADHD is removed. Close medical supervision and careful dosing are crucial here.
Possible side effects and what to look out for
Any medication approved for ADHD in adults can have side effects. Common side effects include:
· Sleep disturbances (especially when taken too late)
· Increased blood pressure and heart rate
· Loss of appetite
If severe side effects occur while taking the medication, the dosage must be adjusted by a doctor. Alternatively, non-stimulant medications such as atomoxetine or guanfacine are available, which often have a different effect on the symptom profile.
Holistic treatment of ADHD
The current guideline emphasises that medication should ideally be combined with psychotherapy. While stimulants help patients to 'get started', coaching supports them in developing strategies for everyday life.
Tips for everyday life with medication:
1. Scheduled breaks: Since the medication masks fatigue, plan breaks before the psychological strain becomes too great.
2. Sleep hygiene: Since sleep disorders are common side effects, a consistent rhythm is essential.
3. Sensory check: Pay attention to whether you react more sensitively to stimuli under the influence (especially with AuDHS).
Conclusion: Treating ADHD with medication is highly effective in indirectly improving attention and concentration via the motivation system. However, the basis for lasting improvement remains the balance between active ingredients, sleep and therapeutic support.
Terms requiring explanation
1. Psychostimulants: Medications that temporarily increase the activity of the central nervous system.
2. Methylphenidate/lisdexamfetamine: The chemical names of the active ingredients behind brand names such as Ritalin, Concerta and Elvanse.
3. Reuptake inhibition: A process in which neurotransmitters remain in the synaptic cleft for longer instead of being reabsorbed immediately.
4. Synaptic cleft: The microscopic space between two nerve cells where information is transmitted.
5. Dopamine and noradrenaline: Neurotransmitters responsible for drive, reward and alertness.
6. Arousal: The general degree of activation or alertness of the nervous system.
7. Circadian sleep disorders: Disorders of the natural 24-hour sleep-wake cycle.
8. Guideline: Medical recommendations for doctors based on the latest scientific findings.
9. Atomoxetine/guanfacine: Non-stimulant medications that are an alternative to traditional active ingredients.
10. AuDHS: A modern term for people who have been diagnosed with both autism and ADHD.
11. Xerostomia: The medical term for dry mouth, a common side effect of ADHD treatment.
12. Bruxism: Unconscious teeth grinding or jaw clenching, often exacerbated by increased arousal under medication.
13. Hypertonia (muscular): Increased muscle tension that can lead to cramps.
Frequently asked questions about ADHD medication.
1. Basics: How do the medications actually work?
What are psychostimulants? These are active substances that increase the activity of the central nervous system. Among the best-known are methylphenidate (e.g., Ritalin, Medikinet) and lisdexamfetamine (e.g., Elvanse). Contrary to previous assumptions, the latest research indicates that they primarily affect alertness and motivation rather than attention filters.
How does reuptake inhibition work? Signals are sent in the brain via the synaptic cleft (the space between nerve cells). Neurotransmitters such as dopamine and noradrenaline transmit these signals. Stimulants prevent these substances from being reabsorbed too quickly. This keeps them active for longer and increases the expectation of reward.
What does "arousal" mean in this context? Arousal describes the degree of inner alertness or excitement. Stimulants increase this level and can thus mask the symptoms of sleep deprivation.
2. Diagnosis and everyday life in adults
Is it worth starting medication in adulthood? Yes, many adults report a significant improvement in their everyday lives. The medication helps to lower the "barrier" to tasks (motivation) and increase stamina. It is often particularly effective in severe cases of ADHD.
What is the 30% rule for ADHD? Put simply, this rule states that the emotional and executive maturity of people with ADHD is often about 30% behind their chronological age. A 30-year-old may therefore sometimes act more like a 21-year-old in stressful situations. Medication can help to close this gap in self-regulation.
Can I manage ADHD without medication? Yes, psychotherapy or targeted coaching is an essential pillar. Current guidelines often recommend a combination of both. For some, non-stimulant medications such as atomoxetine or guanfacine are also an option.
3. Side effects & physical sensations
What side effects can occur? Common side effects include sleep disturbances, reduced appetite, and increased blood pressure and heart rate. In rare cases, gastrointestinal complaints or headaches may also occur.
Can medication change your personality? When taken in the correct dosage, this should not be the case. If you feel "robotic" or that your personality has changed, the dose is too high, or the active ingredient is not suitable for you. A dose adjustment by your doctor is then necessary.
Why do some people feel "great" on stimulants? The increase in dopamine stimulates the reward system. The brain signals: "Everything is possible." However, it is essential not to confuse this feeling with genuine relaxation, as the medication only masks exhaustion.
4. Special features
What does AuDHS mean? It is a term used to describe people who have both ADHD and autism. Medication often has a more complex effect in these cases: when the chaos of ADHD subsides, autistic traits (such as sensitivity to stimuli) can become more noticeable.
How many hours of sleep do I need with ADHD? Generally, about 7–9 hours are recommended. Since ADHD is often accompanied by circadian sleep disorders (a shifted rhythm), good sleep hygiene is crucial, as lack of sleep severely worsens symptoms.
Alcohol and ADHD medication
The combination of alcohol and stimulants is considered risky because they mask each other:
· Dangerous alertness: Stimulants suppress the natural feeling of tiredness that usually occurs when consuming alcohol. You feel more sober than you actually are, which can lead to dangerous overconfidence and higher alcohol consumption (risk of alcohol poisoning). In addition, people with ADHD feel less of the intoxication and more of the dopamine high, which tempts them to continue drinking. This leads to excessive drinking, which is only noticed the next day in the form of a hangover.
· Strain on the heart: Both substances increase the heart rate and blood pressure. In combination, the risk of cardiac arrhythmia and circulatory problems increases significantly.
· Loss of effectiveness: Alcohol can alter the release of the active ingredient in the medication. In some slow-release preparations, alcohol can cause the entire active ingredient to be released too quickly at once ("dose dumping"), which significantly increases the side effects.
Drugs (examples: cannabis and cocaine)
· Cannabis: Many people use cannabis for "self-medication" to stop their thoughts from racing. However, when combined with stimulants, it can lead to psychological interactions such as paranoia, panic attacks or a deterioration in cognitive performance. In addition, the combination of "up" (stimulant) and "down" (cannabis) puts a massive strain on the heart and circulation.
· Cocaine/amphetamines: As these substances have a similar effect to ADHD medication, this can lead to a dangerous overlap. The reward systems in the brain are flooded, which significantly increases the risk of addiction and can cause permanent damage to neurotransmitters.
Important practical information
When treating ADHD in adults, transparency with the doctor is essential. A stable medication level can reduce the urge to seek out addiction (sensation seeking), but only if the medication is not disrupted by additional consumption.
5. Practical tips (the rules)
· The 2-minute rule: If a task takes less than two minutes, do it immediately. The medication will help you overcome your inner resistance.
· The Starbucks rule (body doubling): Many people with ADHD can work better in busy environments (such as cafés) because the presence of others serves as an "anchor" for their attention.
· Be careful with caffeine: Since stimulants already increase arousal, additional caffeine can lead to heart palpitations or inner restlessness.
Further questions from those affected
· What is the 24-hour rule for ADHD? Often, a concept for impulse control: wait 24 hours before making a significant decision or responding to a provocative message.
· How do I know if I need ADHD medication? If the psychological strain in everyday life (job, relationship, household) remains too high despite coaching and strategies.
· When is the best time to sleep for ADHD? There is no set time, but consistency is essential, as ADHD brains often "wake up" late (owl pattern).
· What do people with ADHD need most? Understanding, structure and often support in regulating dopamine and motivation.
· Is rudeness a symptom of ADHD? Indirectly, yes; impulsive interruptions or forgetfulness can be misinterpreted as rudeness.
· Can ADHD meds cause personality changes? If the dosage is too high, they can have a "dulling" effect. However, the goal is a more functional self, not a different character.
· Why are some people against ADHD medication? Often, it is because of stigma, fear of addiction, or the misconception that ADHD is just a parenting problem.
· What causes the development of ADHD? Primarily, genetic factors and neurobiological differences in brain signal transmission.
· What is the "red flag" for ADHD? A chronic feeling of failure despite high intelligence or massive chaos in self-organisation.
· What is the 30% rule in ADHD? The theory is that executive functions (self-regulation, time management) in people with ADHD often lag about 30% behind their actual age.
· Is it worthwhile for adults to take ADHD medication? Yes, it can massively improve quality of life by increasing reward expectations and making tasks seem more "doable".
· What is the most challenging age for ADHD? Often in young adulthood, when external structures (school, parental home) disappear, self-organisation is required.
· What are the 4 Cs of ADHD? Mostly: Control, Consistency, Compassion and Consequences as the pillars of management.
· What are the 5 Cs of ADHD? In addition to the 4 Cs, confidence is often added.
· What is the two-minute rule for ADHD? A strategy against procrastination: if a task takes less than two minutes, do it immediately.
· What is the burnout cycle in ADHD? An interplay of hyperfocus/overexertion and complete exhaustion, often fuelled by masking (adapting to neurotypicals).
· Are people with ADHD happier? Not necessarily; ADHD often brings enthusiasm, but without treatment, it also brings a higher risk of depression.
· What jobs are suitable for people with ADHD? Professions with a lot of variety, clear deadlines or creative freedom (e.g. emergency medicine, design, entrepreneurship).
· Why do doctors prefer Vyvanse (Elvanse)? Elvanse (lisdexamfetamine) often has a gentler and longer-lasting effect because it must first be activated in the body, which reduces the potential for abuse.
· What are the 7 signs of ADHD? Commonly cited: inattention, impulsivity, hyperactivity, disorganisation, emotional instability, forgetfulness, and time blindness.
· What is the 20-minute rule for ADHD? Commit to doing an unpleasant task for only 20 minutes. It is often easier to continue after that.
· What is body doubling? Body doubling is a management strategy for people with ADHD. It involves working on your own task while another person (physically or virtually) is present in the room. This person acts as a passive "focus anchor". Their mere presence helps you overcome executive dysfunction and stick with a task without the other person having to intervene actively.
· What is the coffee shop effect? The coffee shop effect refers to the conscious use of moderate background noise (ambient noise) and a lively environment for self-regulation. Environmental stimuli help the ADHD brain achieve an optimal level of arousal. The "noise" occupies the restless part of the brain, allowing the rest to work with greater concentration.
· What is Starbucks syndrome? In contrast to the above-mentioned working techniques, Starbucks syndrome is a profound side effect of drug treatment. It usually occurs when the dosage of psychostimulants (such as methylphenidate) is too high. Those affected appear excessively calm, apathetic, indifferent or "zombified" – similar to the effects of a caffeine overdose.
· How can I recognise Starbucks syndrome? If you or your child feels that your personality is "under a hood" or remote-controlled and emotionally numb while taking the medication, this is referred to as Starbucks syndrome. This is a clear warning sign of incorrect medication or overdose and should be discussed with a doctor immediately to adjust the dose or active ingredient.
· Can ADHD affect bowel movements? Yes, diarrhoea is caused by stress or the stimulating effect of medication on the digestive system.
· What does "high-functioning" ADHD look like? People who appear successful on the outside, but at the cost of massive overexertion and internal exhaustion.
· How many hours of sleep should someone with ADHD get? Also, 7–9 hours, even if falling asleep and staying asleep is often difficult.
· Can I manage ADHD without medication? Yes, through behavioural therapy, coaching and lifestyle adjustments, although medication often lays the foundation for this work.
· Why should people with ADHD avoid caffeine? Caffeine also has a stimulating effect; in combination with medication, it can lead to overexcitement and palpitations.
· Which vitamins are suitable for adults with ADHD? Omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, zinc and vitamin D are often recommended for support (after consulting a doctor).
· When is the ADHD brain fully developed? Often not until around the age of 30, significantly later than in neurotypical people.
· What is the rarest symptom of ADHD? It is difficult to define, but extreme sensitivity to noise or "hyperfocus on the wrong things" is often underestimated.
· Why do people with ADHD have problems with hygiene? Executive dysfunction makes routine tasks such as showering or brushing teeth an insurmountable hurdle (low reward).
· Does ADHD affect urination? Some report more frequent urination due to tension or the effects of medication.
· Can ADHD medication cause muscle cramps? Yes. Aderall cramps are well known. Since all psychostimulants activate the body, muscle tension increases. This can lead to cramps or painful teeth grinding. Since these medications are strictly regulated in the United Kingdom (unlike Adderall), the dose should be checked by a doctor if such symptoms occur.
· Why does my body suddenly smell like onions? Stimulants can alter the composition of sweat, leading to a more intense odour.
· Do medications cause body odour? Increased sweating (stimulation of the nervous system) can alter body odour.
· Does altered body odour only occur with Adderall? No. Most medications used to treat ADHD, especially psychostimulants such as methylphenidate, can increase sweat production. This is due to activation of the sympathetic nervous system, which triggers the "fight-or-flight" response.
· What can be done about it? In addition to increased hygiene, adequate fluid intake often helps to dilute the concentration of breakdown products in sweat. If the odour is extremely disturbing or accompanied by heavy night sweats, the dosage should be reviewed by a doctor.
· Do ADHD medications cause bad breath? Often, along with dry mouth (xerostomia), which can lead to gum problems or tooth decay ("Adderall mouth").
· What is dry mouth in ADHD medication? Often referred to as "stimulant mouth", active ingredients such as methylphenidate or lisdexamfetamine lead to reduced saliva flow. This is a common side effect, especially at the beginning of treatment or at high doses.
· How can you fall asleep while taking ADHD medication? By taking it at fixed times, using relaxation techniques and avoiding blue light in the evening.
· What is the most significant side effect of Adderall? Often loss of appetite, insomnia or a dry mouth.
· Why do I feel fantastic on Adderall? It floods the reward system with dopamine, triggering a sense of competence and energy.
· Does Adderall permanently alter brain chemistry? At therapeutic doses, the changes are usually reversible, but the brain uses the medication as a "crutch".
· Who should not take Adderall? People with severe heart defects, untreated high blood pressure or a history of addiction.
· What counteracts the effects of ADHD medication? Acidic foods (such as orange juice and vitamin C) can hinder the absorption of certain active ingredients in the stomach.
RELATED ARTICLES:
